- Mazda Engine Serial Number Locations
- Mazda Engine Serial Number Location Number
- Mazda 3 Engine Serial Number Location
- MX5 VIN plate is located on the offside of the bulkhead on a silver metal plate held by two silver rivets. A VIN repeat can be found on sticker on the inside of the offside 'B' post. Varies, but the engine code can generally be found either on the rear offside or the nearside rear of the block.
- The engine serial number is made up of several components. For example, a full engine serial number could be PJ56P. The engine serial number is the complete number shown. This is made up of. The list number or build list, typically 2 to 4 letters followed by 4 or 5 numbers; a letter identifying the country; a series of numbers showing.

Hi there, What I feel has happened here, is that at some time this car has been re engined through a dealership, often when this happens the dealer get a factory new engine that has never been serialized, this is the responsibility of the dealer to stamp the new engine No on, and this is often forgotten, ( I have come across this before, here in Australia) here if this happens we have to. Decoding Your Mazda RX-7 Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) This page will assist you in decoding the VIN# of your RX7. Serial Number: RX7 Chassis Number Identification. Production Date. Mar / '78 - Jun / '79. 500001 - 568500. Jun / '79 - Sep / '80. 568501 - 650000.
| Type | Family | Name | Displacement (cc) | Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V2 | V-twin | BA EA/EB | 356 577 | 1958–1963 |
| MB HB | 1105 1400 | |||
| I4 | early OHV | DA/DB RA SA TA UA/UB VA | 358 586 782 1139 1484 1985 | 1959–1967 |
| later OHV | PB TB | 987 1169 | 1961–1974 | |
| xC | PC TC UC/D4 UB/D5 NA VB | 985 1272 1415 1490 1586 1796 | 1965–1984 | |
| E | E1 E3 E5 | 1071 1296 1490 | 1980–1987 | |
| F | VC MA FE F2 FS FP RF R2 | 1769 1970 1998 2184 1991 1839 1998 2184 | 1977–2002 | |
| G | G6 G5 GY | 2606 2500 2494 | 1989–1999 | |
| B | B1 B3 B5 B6 B8/BP | 1138 1324 1498 1597 1839 | 1985–2005 | |
| Z | Z5 ZL ZM | 1489 1498 1598 | 1995–2014 | |
| MZR | ZJ ZY Z6 L8 LF L3 | 1349 1498 1598 1798 1999 2261 | 1995– | |
| Diesel I4 (licensed Perkins) | Mazda | S2 XA HA | 2209 2522 2977 | 1970–1984 |
| V6 | J | JF J5 JE | 2000 2500 2954 | 1986–1994 |
| K | K8 KF KJ KL | 1845 1995 2300 2497 | 1991–2002 | |
| Wankel | Mazda | L8A 10A 12A/12B 13A 13B 20B 26J/26B Renesis | 798 982 1146 1310 1308 1962 2622 1310 | 1963– |
Mazda makes both piston and Wankel 'rotary'engines. This page summarizes the various engine families and variations.

Piston engines[edit]
Although Mazda is well known for their Wankel 'rotary' engines, the company has been manufacturing piston engines since the earliest years of the Toyo Kogyo company. Early on, they produced overhead camshaft, aluminum blocks, and an innovative block containing both the engine and transmission in one unit. This section summarizes piston engine developments. Note that only Mazda's V-twin, Inline-4, and V6 configurations have made it to market. The company has engineered and completed a W12 engine by 1990 for use in their proposed Amati luxury car brand. Due to financial hardships during that time, the luxury brand was abandoned as well as those two engines.
V-twin[edit]
Like several other Japanese makers, Mazda produced V-twin engines for their three-wheeled delivery vehicles of the 1950s. These were also used in some of the tiny keicars of the 1960s. These were essentially motorcycle engines, and were largely superseded by water-cooled straight-4 engines in a few years, except for in the Mazda R360 which remained in production until 1969 especially for the handicapped.
- V-twin - 356 cc—1.4 L air-cooled V2 (1958-1969)
Inline-4[edit]
Mazda's strength since the 1960s has been in its line of Inline-4 engines. Beginning with a tiny 358 cc kei car engine, one of the smallest ever made, Mazda continues to this day to be a leading developer of this type of engine.
- OHV engine - 358 cc–1.2 L OHV I4 (1961–1974)
- xC engine - 1.0 L–1.8 L SOHC I4 (1965–1983)
- E engine - 1.1 L–1.5 L SOHC I4 (1980–1987)
- F engine - 1.6 L–2.2 L SOHC/DOHC I4 (1977–2002)
- RF engine (including MZR-CD) - Diesel - 1983 - 2009
- G engine - 2.5 L–2.6 L I4 (1989–1999)
- B engine - 1.1 L–1.8 L SOHC/DOHC I4 (1985–2005)
- Mazda Z engine (MZR) - 1.3 L–1.6 L DOHC I4 (1995–2011)
- Mazda L engine (MZR) - 1.8 L–2.5 L DOHC I4 (2002–2011)
- Japan Kei car engine - Suzuki I4
- Diesel - 1.4 L–4.6 L I4
- YF - 2.0 L I4 for Mazda Tribute
- SkyActiv-G - 1.3/1.5/2.0 L I4 (2011–present)
- SkyActiv-G - 2.5 L I4 (2013–present)
- SkyActiv-D - Twin Turbo Diesel - 2.2 L I4 (2012–present)
V6[edit]
Mazda has created three families of in-house V6 engines. As of 2000, they build and use the Ford Duratec V6 design.
- J engine - 2.0 L–3.0 L 60° V6 (–1995)
- K engine - 1.8 L–2.5 L 60° V6
- Diesel V6 - 4.1 L–5.5 L ZB/ZC V6
- AJ/MZI - 2.5 L and 3.0 L V6 - The Mazda version of the Ford DuratecDOHC V6. The 3.5 L MZI is the Ford Cyclone engine.
Wankel engines[edit]

Mazda is the only producer of successful Wankel engines, positioning them as a prime sports car powerplant. All of Mazda's Wankels are based on their first design of the 1960s, though there have been significant developments over the four decades. After Mazda RX-8 production ceased in 2013, Mazda has carried on with testing prototypes to re-introduce the rotary as part of the 'SkyActiv' lineup, dubbed SkyActiv R, displacing 1600 cc and featuring direct injection, laser ignition and forced induction.
- Wankel family - 1.0 L-2.0 L Wankel (1967–present)
- 10A - 1.0 L (1967–1973)
- 0813 - 1.0 L (1968–1972)
- 13A - 1.3 L (1970–1972)
- 12A - 1.1 L (1970–1985)
- 13B - 1.3 L (1973–2002)
- 20B - 2.0 L three-rotor (1990–1996)
- R26B - 2.6 L four-rotor (1991 24 Hours of Le Mans winner)
- Renesis - 1.3 L (2004–2013)
- Mazda Skyactiv-R - (2022?–present)
Gasoline Diesel Engine[edit]
Vehicle Identification Number
The vehicle identification number legally identifies your vehicle. The number is on a plate attached to the cowl panel located on the left corner of the dashboard. This plate can easily be seen through the windshield
Motor Vehicle Safety Standard Label (U.S.A. and Canada)
For vehicle identification number beginning with JM1
For vehicle identification number beginning with 3MZ *
*1 Check the vehicle identification number on the vehicle identification number plate. Refer to Vehicle Identification Number on .
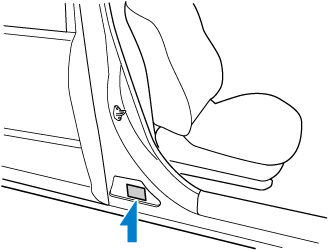
Chassis Number
Open the cover shown in the figure to check the chassis number.
Vehicle Emission Control Information Label (U.S.A. and Canada)
Tire Pressure Label
For vehicle identification number beginning with JM1
For vehicle identification number beginning with 3MZ *1
*1 Check the vehicle identification number on the vehicle identification number plate. Refer to Vehicle Identification Number on .
Engine Number

Specifications
Engine Electrical System *1 Q-85 is designed for i-ELOOP system. Only Q-85 should be used to ensure correct operation of i-ELOOP system. Consult an Authorized Mazda Dealer for details. ...Other materials:
Mazda Engine Serial Number Locations
Buckle Switch Inspection
Driver Side 1. Switch the ignition to off. 2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.. 3. Remove the front seat.. 4. Remove the front buckle.. 5. Inspect for continuity between the buckle switch terminals using a tester. If not as indicated in the table, replace the driver sid ...
Mazda Engine Serial Number Location Number
Bluetooth®
Bluetooth ® Hands-Free outline When a Bluetooth ® device (mobile phone) is connected to the vehicle's Bluetooth ® unit via radio wave transmission, a call can be made or received by pressing the talk button, pickup button, or hang-up button on the audio remote control switch, or by operating ...
Mazda 3 Engine Serial Number Location
Blind Spot Monitoring (Bsm) Off Switch Removal/Installation
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.. 2. Remove the switch panel in the direction of the arrow shown in the figure. 3. Disconnect the connector. 4. Remove the BSM OFF switch in the direction of the arrow (2) shown in the figure while pressing the tabs in the direction of the arrow ...




